EEG detection systems. 1-1: major components of the seizure advisory
EEG detection systems. 1-1: major components of the seizure advisory
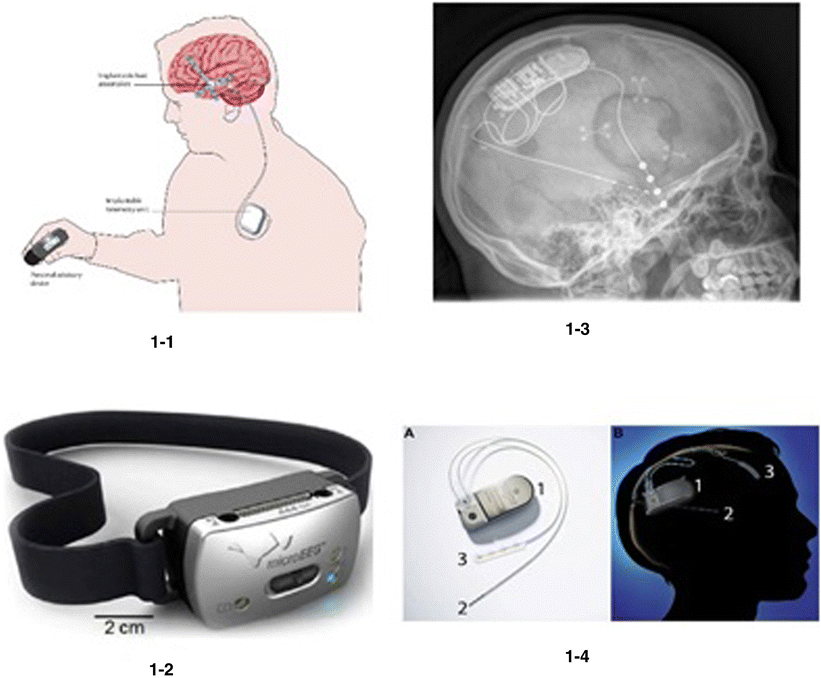
Download scientific diagram | EEG detection systems. 1-1: major components of the seizure advisory system: intracranial electrode arrays (location shown by grey areas) were used to collect intracranial EEG data on the cortical surface. Leads were connected to a subclavicularly placed implanted telemetry unit, which wirelessly transmitted data to an external, hand-held personal advisory device. The external device received the telemetered EEG and displayed the resultant information as a series of advisory lights—blue (low), white (moderate), or red (high) indicators—in addition to an audible tone or vibration, or both [45•]. 1-2: microEEG attached to a headband [43••]. 1-3: RNS stimulator with depth and surface electrodes. Notes: example of a patient with both neocortical surface electrodes and hippocampal depth electrodes [46]. 1-4: (A) NeuroPace RNS Neurostimulator. (B) Implanted schematic. The RNS system is unique due to its ability to respond as needed instead of remaining active continuously. The RNS device (1) is attached to depth electrodes (2) and/or cortical strip leads (3), and when seizure activity is detected, the RNS responds with electrical stimulation to prevent neuronal synchronization and onset of seizure activity. Reprinted with permission from NeuroPace [47] (copyright permission required for use of figure) from publication: Seizure detection: do current devices work? And when can they be useful? | Purpose of review: The unpredictability and apparent randomness of epileptic seizures is one of the most vexing aspects of epilepsy. Methods or devices capable of detecting seizures may help prevent injury or even death and significantly improve quality of life. Here, we | Seizures, Devices and Epilepsy | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
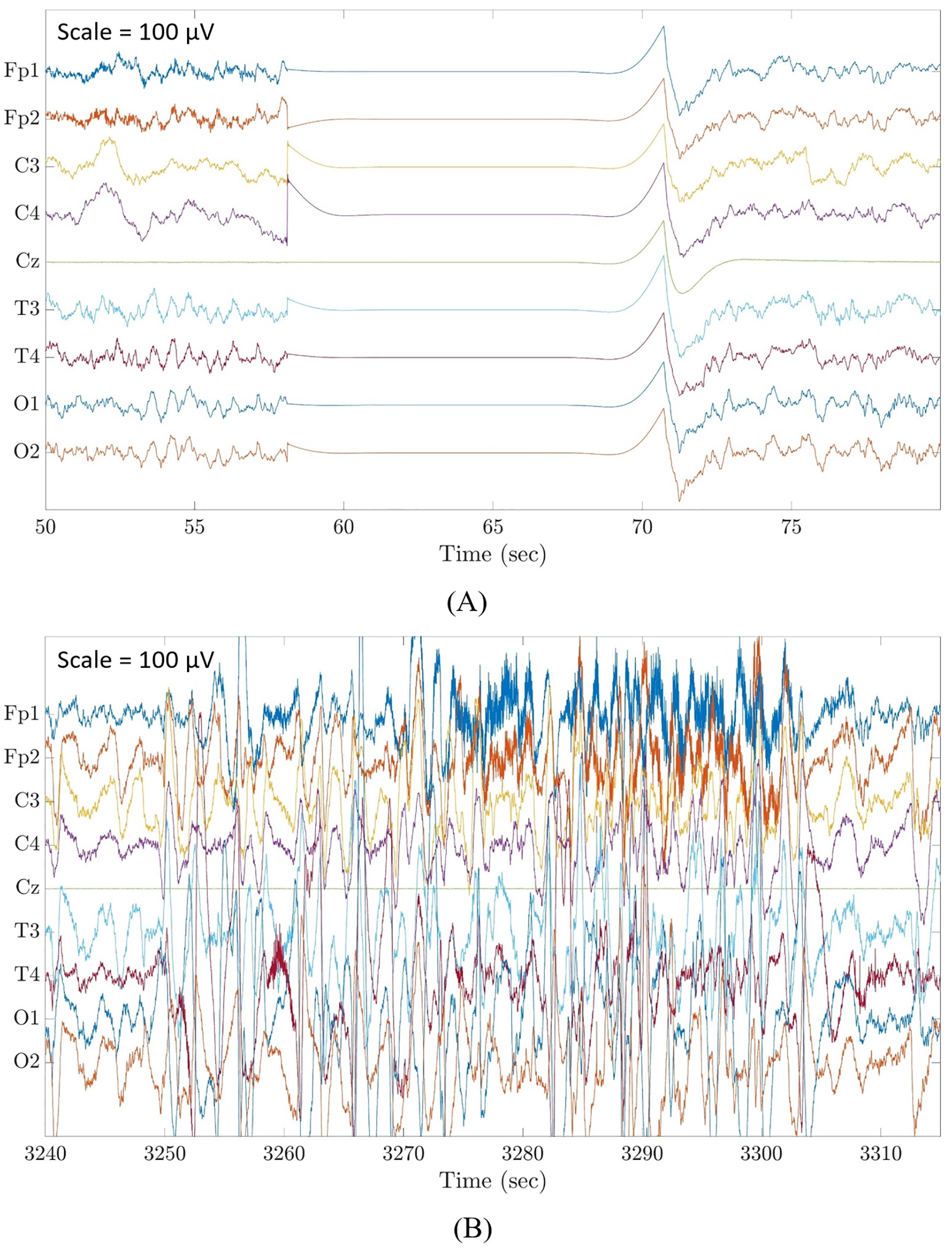
Automated detection and removal of flat line segments and large amplitude fluctuations in neonatal electroencephalography [PeerJ]

Neural Fragility as an EEG Marker of the Seizure Onset Zone

Full article: Automated human mind reading using EEG signals for seizure detection
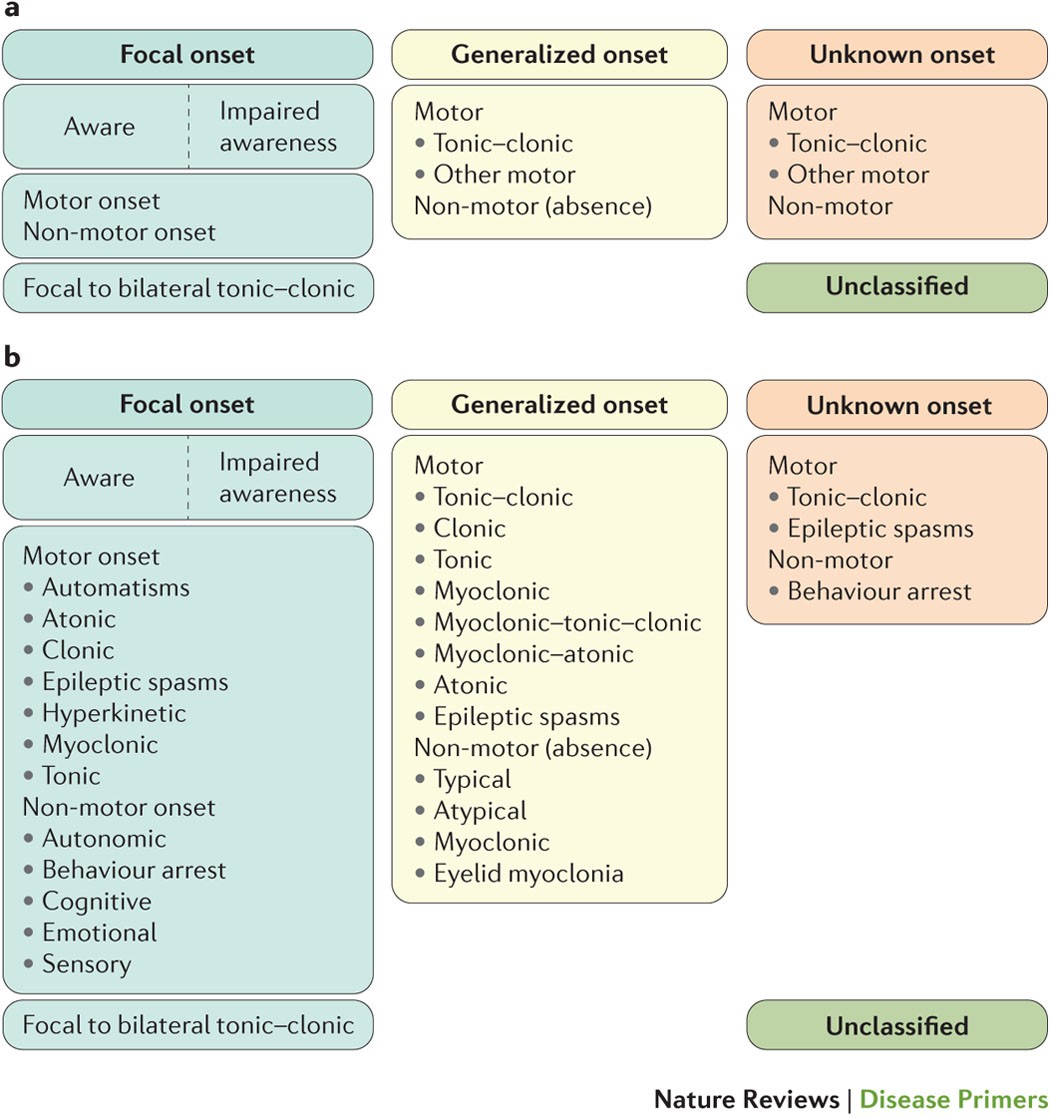
Epilepsy Nature Reviews Disease Primers

Structure-function coupling reveals seizure onset connectivity patterns

Seizure Control in Neonates Undergoing Screening vs Confirmatory EEG Monitoring
Detecting seizures and interpreting EEGs, th

Evaluation of the feasibility, diagnostic yield, and clinical utility of rapid genome sequencing in infantile epilepsy (Gene-STEPS): an international, multicentre, pilot cohort study - The Lancet Neurology
.jpg)
Classifying the Epilepsy Based on the Phase Space Sorted With the Radial Poincaré Sections in Electroencephalography - Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences


